Brief Introduction of Textile Recycling Methods and Technologies
1636
Mar 12,2023
The landfill of large quantities of garments each year contributes to the rising greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere, thus aggravating the global warming issue. Although only a meager of textiles are recycled, the existing recycling methodologies are primitive to process large amounts of apparel waste. Therefore, the need for more advanced and sophisticated technologies to process them is on a rise.
State of the art technology clusters
Broadly speaking, textile recycling can be classified into mechanical and chemical recycling. Mechanical recycling involves shredding of waste textiles to fibres, which can then be mixed with a virgin fibre, in order to compensate for the physical property deterioration during the mechanical step, for further use, whereas chemical recycling involves the usage of chemicals at certain conditions to reform the worn-out textiles into useful form (fibres, value-added chemicals or fuel components).
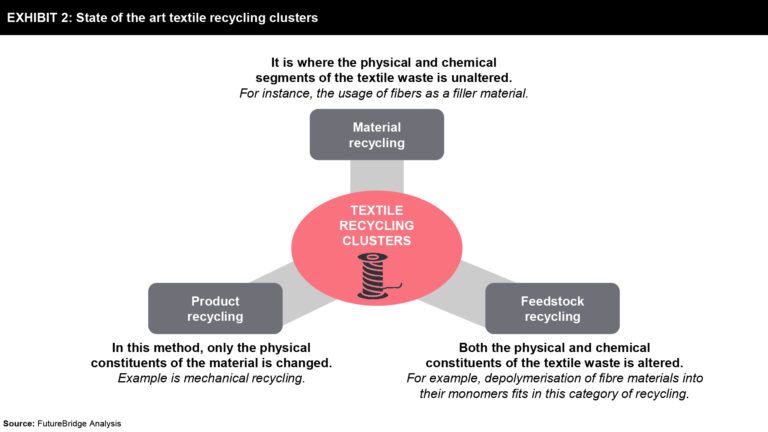
On the other hand, the textile recycling processes can be categorized into three types based on the degree of processing in each operation, as mentioned in Exhibit 2.
Another alternative to recycling operation is the recovery process, where the textile waste is subjected to thermal recovery by employing a recovery operation in waste-to-energy power plants. It is still being practiced; however, it is very likely to be commercialized at full scale in a few years down the lane.
Current and future recycling technologies
The future recycling methods will essentially focus on the molecular separation of the different components in the fabric by employing a combination of existing chemical recycling with fast, simple, and energy-intensive engineering that makes the process continuous and reliable. Also, the emergence of new technologies such as the internet of things will enable textile waste sorting and identification in an efficient manner, which will aid the textile recycling value chain. Exhibit 3 provides a detailed overview of future textile recycling methods.
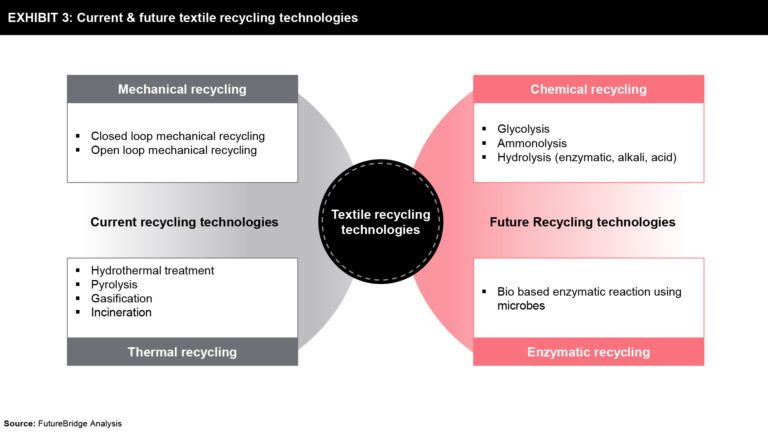
Some of the existing/ current technologies are:
· Advanced mechanical recycling:
· Closed-loop mechanical recycling: It involves the disintegration of waste textiles into discrete fibres. Unlike the existing mechanical methods, it yields fibres without losing its mechanical properties, especially rigidity and strength
· Open-loop mechanical recycling: It employs cutting fibres before subjecting them to the melt-blowing process, where it is broken down to individual fibres. After which, it is web formed and then dried to obtain the final product. it is used, for instance, to make individual pads for mattresses
· Thermal recycling methods:
· It aims in generating energy products like fuel or the heat itself. The three prominent technologies to be used for this purpose are hydrothermal treatment, pyrolysis, and gasification.
Some of the promising future technologies are:
· Chemical recycling methods
· Glycolysis: The glycolysis products from the PET waste will be used to synthesize degradable co-polyesters.
· Ammonolysis: Being carried out in the presence of amino acids, it will be primarily used to convert nylon 6 and nylon 6,6 to other value-added chemicals
· Hydrolysis: It is very versatile, as it can be used to process mixed fabrics like cotton, wool, and polyester. Even though it is of different types, the three main kinds which are gaining more traction in the recent days are – enzymatic hydrolysis, alkali hydrolysis, and acid hydrolysis
· Enzymatic treatment:
· Enzymes are biocatalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions. Also, they are highly selective so they only act on particular substrates and produce only the desired products. For instance, cellulose which can be obtained from both fungi and bacteria category can be used in cellulose hydrolysis
Source: www.futurebridge.com